ART-NANO
VALVE METALS ANODIC TREATMENT AT TRANSIENT
CURRENT LOADS IN ELECTROLYTES CONTAINING
NANOSIZED CARBON ADDITIVES
Anodic treatment is the most promising method in comparison with existing techniques of coatings application to aluminum, magnesium, titanium alloys. This method allows to obtain coatings with good mechanical, dielectric, heat resistance, protective and decorative properties. The endurance of the coatings applied to aluminum and magnesium alloys exceed s that of all the existing materials in the modern technological process.
MAIN APPLICATION AREAS
- Petroleum and coal industry - the creation of corrosion and wear-resistant coatings for drilling, coal and oil production, oil refining equipment.
- Rocket engineering - developing heat-,erosion- and wear-resistant coatings for rocket engines.
- Mechanical engineering - friction couples, slide bearings, gears, forcers, cylinders, internal combustion engines' face seals, tools and machines for different purposes in shipbuilding, aircraft industry, agricultural machinery details.
- Metallurgical engineering - permanent casting equipment, molted casting bars, furnace lining, heat shields, etc.
- Construction industry - Aluminium profiles, assembly design, and other constructions' processing. Windows production. Protective and decorative coatings.
- Light industry - thread guides, shuttles and other parts of the textile and sewing machinery.
- Medicine - Surgical implants.
|
 |
Technological processes developed
with ART-NANO application allows
To develop multifunctional composite anodic-oxide coatings with unique physical, mechanical and operational properties:
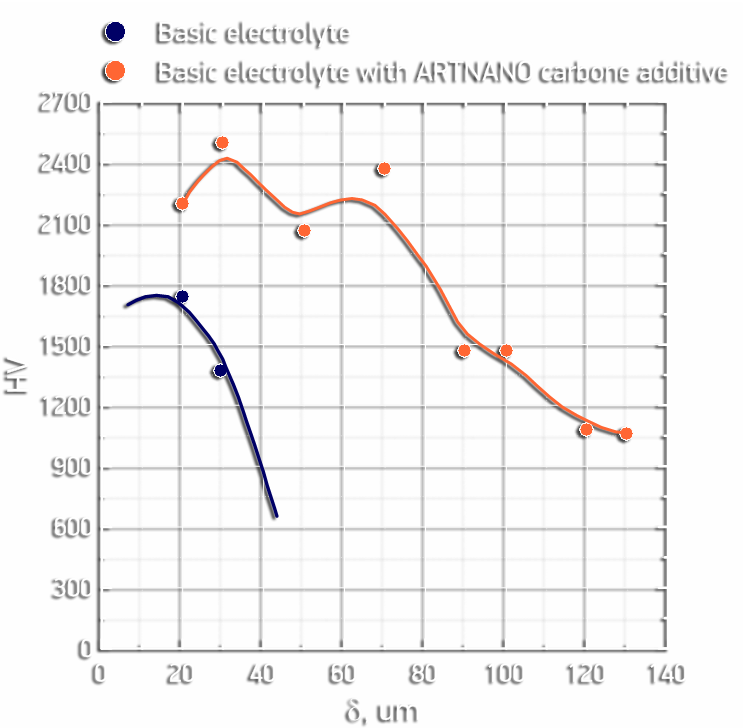
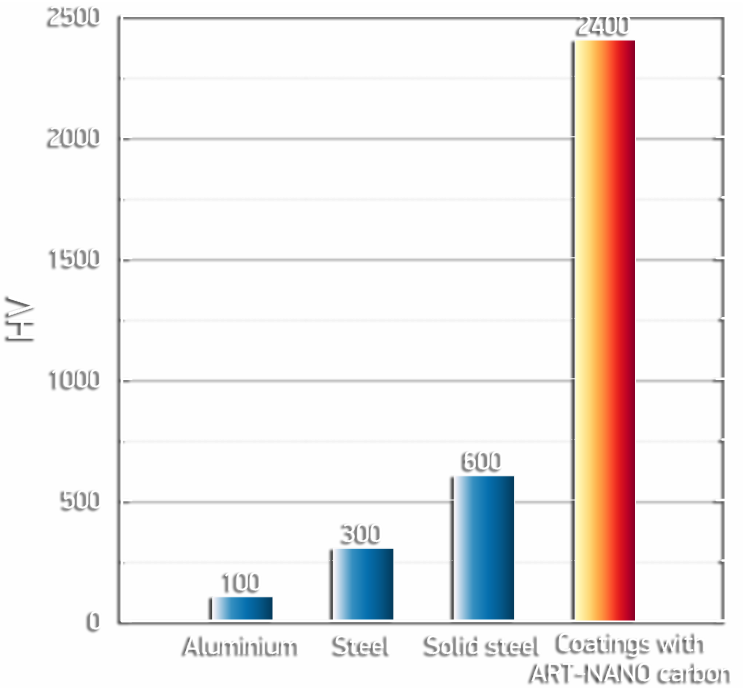
- Microhardness up to
2400 HV;
- Coating adhesion to the substrate at the level of 350-370 MPa
;
- The coating boundary friction coefficient in pair with steel
0.02-0.03;
- The coating dry friction coefficient in pair with galvanic chromium less than 0.05. Wear rate 10-11-10-10 mg/m;
- A breakdown voltage of up to 5 kV.
ART-NANO carbon additive introduction
into the electrolyte also allows:
- To structure the surface.
- Increase the rate of coatings formation in 1.5-2 times.
- Reduce energy consumption in 1.7-2.5 times due to the working current density and voltage reduction.
- Achieve nanoscale coatings and coating thicker than 300 microns in all types of aluminum alloys, including high-silicon casting alloys.
- To develop coatings for outer and inner surfaces of friction units of different shapes.
- Maintain the original dimensions of parts after coating application.
- Use environmentally friendly electrolytes.
| Shut-off gas fitting ball |
Press molds and the internal combustion engine details |
Aluminum profiles protective and decorative treatment |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |